Offering an online chat service to your audience is a powerful way to increase engagement. Chat protocols play a crucial role in enabling real-time communication by providing a safe space that allows messages to be transmitted instantly between users. These protocols also define the specific rules and formats for these exhanges, ensuring that messages are sent and received efficiently and securely.
Staying updated with the most popular chat protocols is essential for both developers and businesses to ensure compatibility, security, and optimal performance. By keeping up with these advancements, businesses can provide more reliable and efficient communication tools, meet the growing demands of users, and stay competitive in the market.
Learn more about different instant messaging systems and find out which one suits your needs best.
Three Ready-to-Use Chat Apps
There are significant disadvantages to using an open messaging protocol (i.e., an open standard for messaging). This kind of technology often requires significant development effort and testing, and that’s fine if you’re interested in developing your software, but isn’t very practical when you have a tight deadline.
What if you need to offer a real-time chat experience by tomorrow? That’s where these three chat apps come to play.
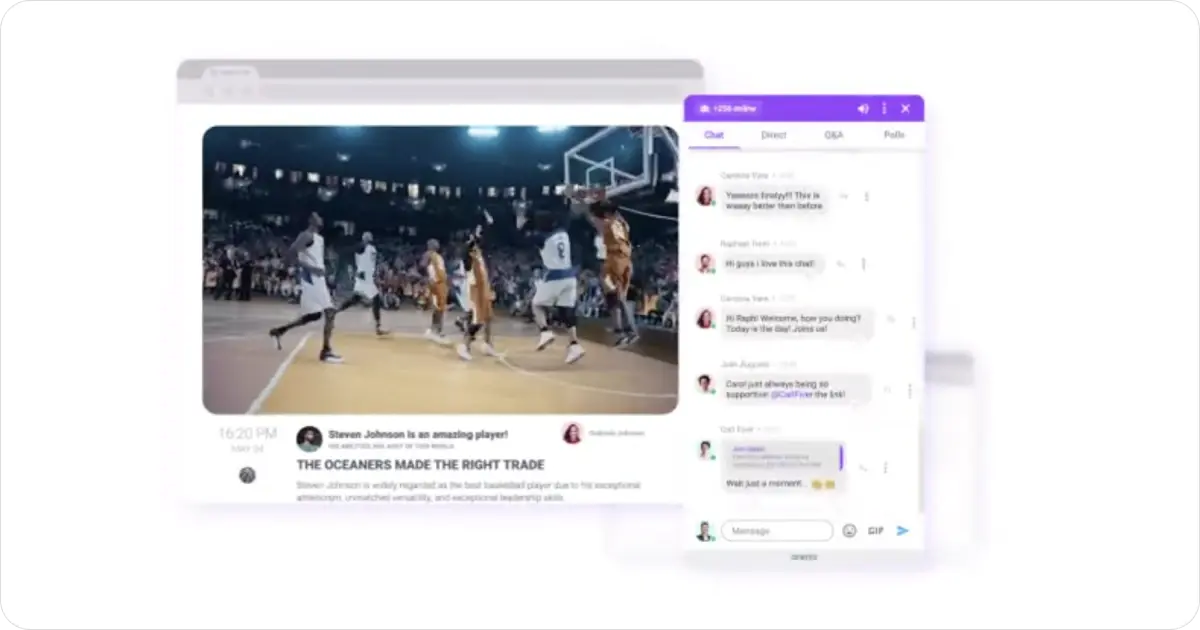
1. Arena Live Chat
- Advantages: robust message interface for groups, Chat API, notifications and moderation features. Arena is one of the first chat services to offer AI functionality!
- Disadvantages: in July 2023, there is no iOS or Android app for Arena’s Dashboard. Fortunately, Arena is lightweight and fast, so it works beautifully in a mobile browsers.
Arena Live Chat is a chat client designed for groups and events. It is designed to be lightweight and easy to install and configure. If you are running hybrid events or online events to engage your employees or customers, Arena Live Chat is a great choice.
With features such as polls, Q&As, GIF reactions and moderation capabilities, Arena Live Chat is a powerful community chat software for brands and publishers looking to grow their audiences.
2. Facebook Messenger
- Advantages: integrated with Facebook, so there is no need to set up additional accounts, supports video chats and payments between users.
- Disadvantages: some features, such as payments, are only available in certain countries, some users are skeptical about Facebook’s privacy track record, and may drain mobile device batteries fast. It is not an open messaging protocol, so it has development limitations.
Facebook Messenger is one of the most popular live chat platforms in the world. According to one estimate, there are over one billion Facebook Messenger users today. Since it offers so many features, it is no surprise that Messenger is a relatively large app – it takes over 100 MB in storage in most cases.
From a marketing perspective, Facebook Messenger is interesting because there are third-party services that make it easy to create chatbots. This business approach to Facebook Messenger can boost your lead generation and improve basic customer service. For brands with a large Facebook following, Facebook Messenger has much to offer.
3. Google Messages
- Advantages: the chat client supports private messages, group chats, payments, and searching for information on businesses (e.g., restaurants)
- Disadvantages: some users have complained about a poor search experience and glitches with video calls.
Initially launched in 2014, Google Messages has gradually become one of the most popular messaging apps. Also known as Messages by Google, the app has an estimated 1 billion installs. In 2021, instant messenger added support for an end to end encryption.
Google Messages added support for rich communication services (RCS) in 2019. This enhancement means that the app no longer relies on the cellular network. Google Messages does not require a mobile app – the chat client is available through a browser. Adding support for RCS makes Google Messages more competitive with Apple iMessage.
What if you want to use an open standard for messaging? The following real time chat protocol section introduces you to some of the best options on the market.
Popular Instant Messaging and Chat Protocols
These protocols and services offer different capabilities and require different levels of effort to implement. Some, like IRC, are relatively easy to set up. Most of the other protocols take more effort.
1. WebRTC – Web Real-Time Communication
- Advantages: WebRTC is open source (initially developed by Google), the protocol has relatively sophisticated sound capabilities, and third-party apps can be developed using the protocol.
- Disadvantages: it is a relatively new protocol, and there are relatively few online services based on it.
Launched in 2011 by Google, WebRTC is a communication protocol built for web browsers. The protocol supports video calls, but this functionality requires a separate server. The protocol has significant appeal for software companies looking to build their online services.
2. WebSocket
- Advantages: allows two-way communication faster than the HTTP protocol. It is a lightweight protocol with a 2-byte cost (much less than HTTP), so it is an excellent choice for users concerned about speed and performance.
- Disadvantages: the reliability of WebSocket is limited by the user’s Internet connection.
Among today’s communication protocols, WebSocket is relatively well established. It was launched in 2008 and started to attain widespread adoption in 2010. WebSocket relies on a TCP connection.
3. IRC – Internet Relay Chat
- Advantages: long considered one of the oldest and most reliable messaging services in the market, some support for file sharing.
- Disadvantages: no support for video calls, voice calls, or other advanced features, a declining number of active users.
IRC is often considered the chat platform that made the rise of messaging platforms platform. Established in 1988, IRC is one of the oldest Internet services. According to one estimate, IRC once had over a million users in the early 2000s. While IRC still has some niche uses and specialized communities, it is much closer to email in spirit than a true chat platform.
IRC’s long-term success as a real-time text messaging platform is nonetheless remarkable. If you are building a chat app (or online community) from scratch, studying the longevity of Internet Relay Chat may be worth the time. Remember that the platform was initially developed before broadband Internet access was widely available, so it is not an excellent match for today’s network capabilities.
4. XMPP: Extensible Messaging and Present Protocol
- Advantages: XMPP is an open, flexible protocol and offers a decentralized architecture. Setting up XMPP on corporate networks (instead of the Internet) is also possible for added security.
- Disadvantages: it lacks QoS (quality of service) support, so voice and video call performance is not the same as top-of-the-line VoIP services. In addition, there is no single official client you can use to access the protocol.
XMPP is a modern instant messaging protocol that supports popular chat functionalities like voice calls, video calls, and file transfers. You can build a chat application or instant messengers based on XMPP. Depending on your goals, you could build consumer software or a corporate chat app based on this protocol.
As a form of communication, XMPP can support various uses and optional features. Since it is much less well-known than apps like Google Talk or Facebook Chat, you may have to plan for additional training time to help your users adopt the platform.
5. MQTT – Message Queuing Telemetry Transport
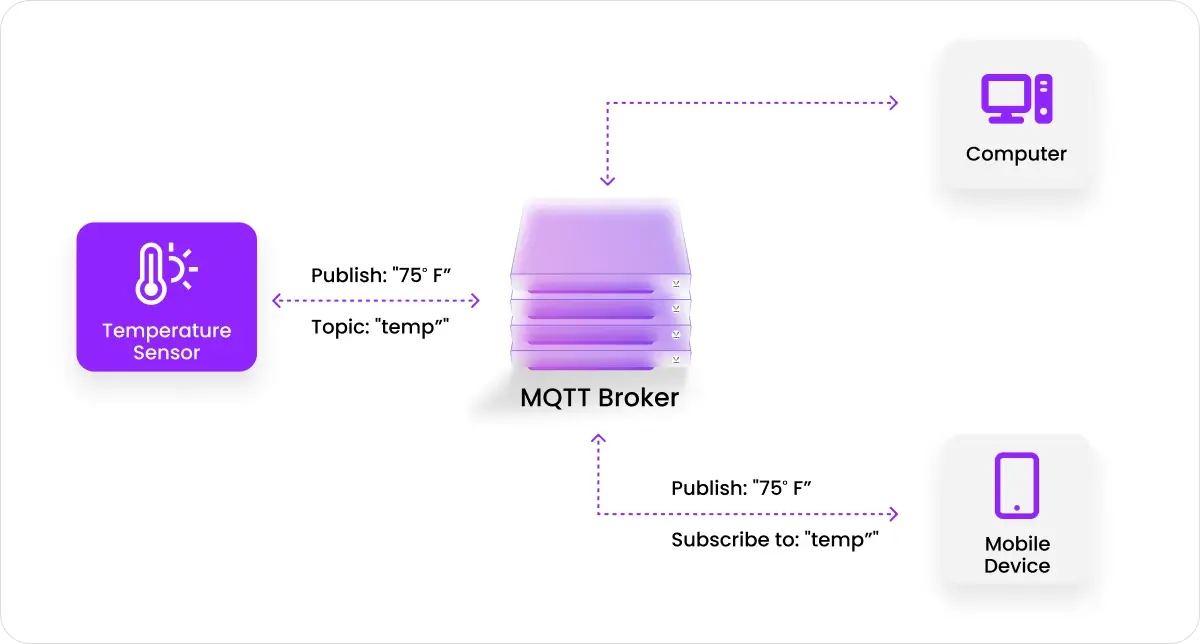
- Advantages: this messaging protocol is excellent for battery-powered mobile devices. MQTT also has high reliability in delivering messages. The lightweight protocol requires minimal CPU resources, best suited for small, low-power applications.
- Disadvantages: no support for video calls, minimal security support, and relatively low speed and latency.
Unlike the other messaging protocols covered above, MQTT is best suited for a specific type of device. MQTT is best used for Internet of Things (IoT) devices and applications. For example, an industrial device at a factory might need the ability to send messages about the temperature or pressure of a specific piece of equipment. MQTT is an excellent choice for that use case. MQTT is not a good choice for consumers.
The relatively weak out-of-box security features are another drawback. Fortunately, this problem can be mitigated by working with security providers. If this drawback is neglected in your implementation, you may introduce more risk into your environment.
6. SIP/SIMPLE
- Advantages: SIP is an open standard compatible with several vendors, it is relatively flexible with the option to support text and video messages, professional oversight by the Internet Engineering Task Force.
- Disadvantages: it is a basic protocol rather than an instant messaging app, so users cannot download it and immediately start using it.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a well-established messaging protocol that has been around for several decades. SIMPLE is a specific implementation of SIP called “Session Initiation Protocol for Instant Messaging and Presence Leveraging Extensions.”
The SIMPLE protocol approach to instant messaging offers both session mode and non-session (i.e., page mode) approaches to messaging. In addition, the SIP SIMPLE protocol also supports presence which means you can detect when users are online. The protocol doesn’t offer built-in support for features like buddy lists (also known as contact lists) or message histories. Therefore, it might be a good option for consumers.
7. AMQP – Advanced Message Queuing Protocol
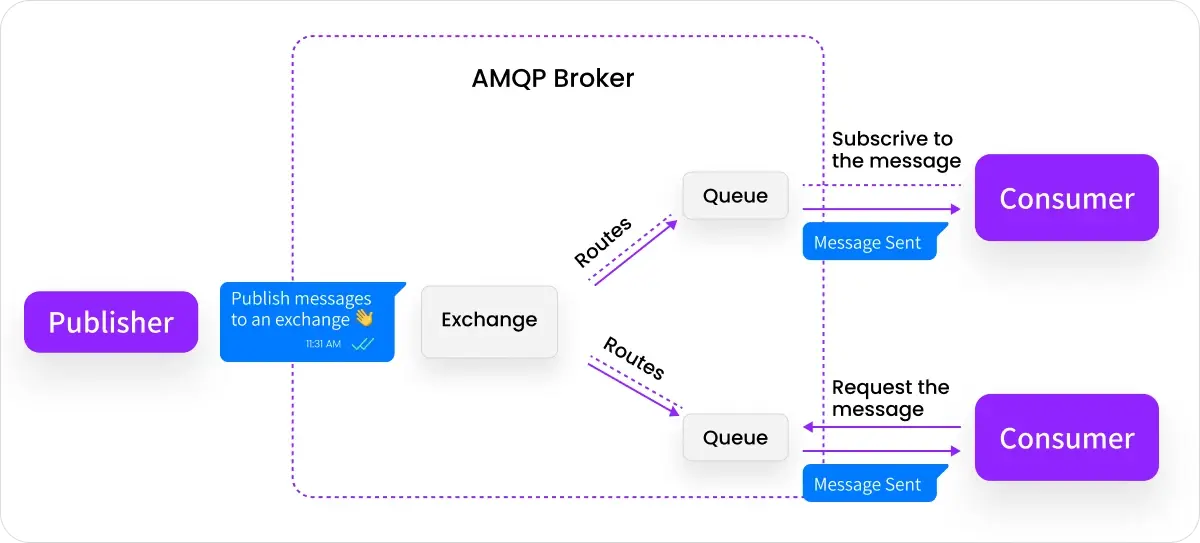
- Advantages: supports secured connections with SSL, supports QoS for message delivery, and simple peer-to-peer delivery.
- Disadvantages: higher bandwidth requirements than other protocols; it is also not backward compatible with older protocol versions.
Announced in 2003, AMQP has an unusual origin: a developer at JPMorgan Chase created it. Other companies, including Microsoft, Progress Software, and Bank of America, became involved in the protocol. Like the MQTT protocol, AMQP runs on the TCP layer of the network.
AMQP’s corporate background means it offers a good foundation for sophisticated applications. AMQP may be a good choice for communication between machines in business communications. The AMQP approach to instant message delivery emphasizes delivery and reliability. As a result, it is a good choice for enterprise instant messaging where accuracy is paramount, like financial use cases.
8. RCS – Rich Communication Services
Offering an online chat service to your audience is a powerful way to increase engagement. Chat protocols play a crucial role in enabling real-time communication by providing a safe space that allows messages to be transmitted instantly between users. These protocols also define the specific rules and formats for these exchanges, ensuring that messages are sent and received efficiently and securely.
Staying updated with the most popular chat protocols is essential for both developers and businesses to ensure compatibility, security, and optimal performance. By keeping up with these advancements, businesses can provide more reliable and efficient communication tools, meet the growing demands of users, and stay competitive in the market.
Learn more about different instant messaging systems and find out which one suits your needs best.
Choosing the Right Chat Service: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right instant messaging system for your business is an important decision. No single chat protocol or app is suitable for every purpose.
Use the assessment criteria below to help you discover the best choice for your needs. For additional insights on deciding whether to buy or build a chat service, see Arena’s article Chat Protocols and Apps: Should You Build or Buy? for additional insights.
Does the Chat Service Have AI Capabilities?
Since ChatGPT arrived in late 2022, AI has become a revolutionary capability. In a chat service, AI can be used in several ways. You can use it to develop questions and encourage discussions. You can also train AI using chat content if permitted by your policies. We’re still in the early days of the generative AI revolution, so make sure your chat service supports this exciting new technology!
Chat Emphasis: Private Messaging or Group Events?
When you compare different chat programs, a key difference quickly becomes apparent. Many chat apps emphasize private conversations between two users. Like Arena Live Chat, other chat services focus more on chat windows for events. That’s not all. Arena Live Chat also offers one on one messages between users.
How Easy Is Installation And Setup?
Few users (or companies!) have the patience to learn a complex chat protocol. Given your other technology projects, asking an IT department to spend weeks or even months learning how to use WebRTC or MQTT may not be realistic.
Instead, choosing an easy chat solution for companies and end-users to access is best. Arena Live Chat is explicitly designed for fast installation. Most companies install it on their website in less than 10 minutes.
What Is The User Experience Like?
The user experience is vital in chat services. Your customers will spend a lot of time interacting with friends (and your employees) through chat. Therefore, investing time upfront in testing the chat app is crucial.
Specifically, we recommend asking non-technical employees to test the chat app. If they have significant difficulties using the chat app, try something else! If your customers have problems using your chat app, they will simply give up and use a different method – like email or phone – to contact your business.
How Does The App Ensure Security?
Security risks are ever-present in the online world, including chat apps. When you give your users a chat window, some people may view that option as an effective attack opportunity. There are a few ways to mitigate this threat to avoid endless security investigations.
A common way to enhance security and privacy concerns is to rely on end-to-end encryption. In addition, you can apply controls to your user IDs. By requiring users to register before joining a chat experience. Finally, don’t rely on the chat window to do all the work. It is also essential to provide security training to your employees to provide a security-conscious experience to end-users.
How To Add a Live Chat To Your Website Today
Now that you know about the most popular chat protocols and chat clients on the market, you have a choice. The first option is to choose a messaging protocol, select a client and spend time customizing the chat app. This option is a good choice if your company has significant technology development resources and the desire to create highly customized solutions.
The second option is to select a fast chat service that is easy to install and requires minimal setup. Find out more about how Arena helps brands and publishers grow their audience.